Courts, like any other public or private organization, often face hectic schedules, busy workloads, and associated challenges, including courthouse space needs. In business, more work often requires more employees; likewise with courts, more work often requires a corresponding increase in the number of judges and staff needed to manage the cases. However, courts must confront unique challenges in predicting workload increases, which are normally driven by factors entirely out of their control, and identifying satisfactory short- and long-term housing solutions in their courthouse planning.
Understanding the Trends Is the First Step
As any court manager or judge knows, courts don’t control their workload, but instead are dependent on external factors. Changes in population, the economy, or law enforcement priorities can all affect the agencies at the end of the justice system chain, especially the courts and their courthouse space needs.
The border between the U.S. and Mexico offers an ideal illustration of the problem faced by growing courts. In recent years, many law enforcement initiatives have been put in place to control illegal border crossing activity and the trafficking of drugs, weapons, and humans along the nearly 2,000-mile stretch of border from San Diego, CA to Brownsville, TX. In an effort to deter these illegal activities, thousands of additional law enforcement agents have been dispatched to the border region. As a result, hundreds of thousands of individuals annually are detained and ultimately face administrative or criminal hearings.
During a court planning project in a town along the southwest border, I was able to go on a ride-along with a border patrol agent. His anecdotes about enforcement activity, combined with my first-hand observations that day, and confirmed by a wealth of published statistics, provided a clear picture of a justice system under pressure. At the federal level, about 75% of all criminal immigration cases nationally are filed in one of the five federal court jurisdictions along the southwest border. At the state and local levels, courts along the border have been affected by additional state civil, family, juvenile, and dependency cases, as well as a substantial number of local criminal cases that do not meet thresholds for federal prosecution.
A Problem Confirmed
My border tour was followed by several focus group meetings at the courthouse, the first of which was with the jurisdiction’s lead prosecutor. The attorney echoed the scenario described by the agent during my ride-along. The number of individuals detained and facing sanctions was skyrocketing, and not just in that area but in towns all along the border in California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. The ensuing discussion with court representatives revealed that the influx of cases affected the operations and space needs of courts at all levels.
Moreover, based on court planning efforts in other parts of the country, I realized that this problem isn’t limited to the southwest border. Oil industry-related population and criminal caseload growth in North Dakota, Medicare fraud enforcement in Florida, and methamphetamine production and distribution in the Midwest are all examples of local or regional crime trends that affect the downstream enforcement and justice system, and potentially require courts to develop space solutions to accommodate more work, more judges, and more staff.
Creative Space Solutions for Courthouse Space Needs
As anyone involved in facility planning knows, the generic logic that more work requires more space is well established. A sustained increase in workload means that more personnel are needed to handle the work, which then results in a need for more workspaces to accommodate the additional staff. But for courts, while an increase in caseload may uniformly translate into operational impacts and a related need for space, accommodating the growth will vary from city to city, and often from building to building, depending on things like the condition of the existing courthouse and the court’s budgetary situation.
In my southwest border court, finding solutions to the court’s space needs proved to be challenging. Facility projects typically involve expansions or major renovations; in these instances, the challenges involve finding the right space to expand into and making sure to plan for an appropriate amount of space to accommodate both current needs and future growth.
In this case, the court couldn’t afford either option, so we had to get creative within the existing space. We proposed a number of potential solutions for a “grow-in-place” strategy, including:
- Adjusting internal policies and practices to incorporate increased sharing of courtrooms by judges (including visiting judges from other jurisdictions)
- Implementing technologies like electronic case filing and case management systems to speed up the civil and criminal docketing processes and ease the burden on court staff
- Creating a collegial chambers layout through renovation, which consolidated space for judges’ staff, conference rooms, libraries, and support areas, which in turn made available space to house additional judges
All of these solutions were eventually implemented, which went a long way toward mitigating the court’s space constraints and satisfying the courthouse space needs.
In a follow-up visit to the courthouse, I found that, when limited funding had become available, the court had also implemented several other small-scale improvements to accommodate the high volume of individuals charged with border-related crimes. These included:
- A sallyport that could accommodate a large prisoner bus carrying up to 40 defendants was carved out of the staff parking area. For ease and safety of the vehicle’s movement, the sallyport was designed as a drive-through enclosure with a separate entry and exit door for the bus.
- A plexiglass prisoner box that could hold as many as 20 in-custody defendants was added to one courtroom. The box had direct and secure access to the central cellblock.
- Procedurally, the court began holding certain proceedings for multiple defendants in the courtroom simultaneously. The individual proceedings were held in quick succession; the ability to have convenient, secure access to those defendants in the central cellblock was key to keeping the proceedings running on schedule.
- Due to the large number of in-custody defendants charged with border-related crimes, the central cellblock was enlarged to include more cells than a similar non-border courthouse would normally have, as depicted in the following plan:
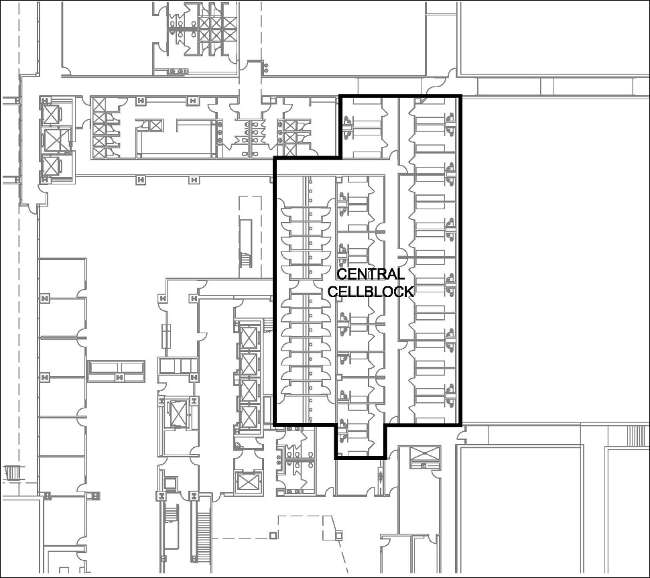
While these “growing-in-place” solutions worked for this court, very different solutions may be more appropriate in other locations, and fortunately, other options exist to satisfy courthouse space needs. Some alternatives that don’t necessarily involve costly or disruptive renovations include:
- Renovating a space to remove individual walled offices and constructing a more open work area with open workstations and collaborative spaces that could accommodate a larger staff within the same area. (Depending on the space and scope, this can often be a minor renovation project with minimal impact on the staff). This project could be combined with enhanced teleworking policies and workstation sharing to save more space, depending on the culture of the court.
- Saving space by sharing administrative responsibilities across multiple components or organizations within a building. Functions such as human resources, payroll, financial operations, information technology, and procurement services are well-suited to sharing, which can streamline staffing and save space.
A Universal Problem
Unfortunately, the combination of more work arriving abruptly and a courthouse with limited capacity to respond is a condition that I encounter quite often. Effective courthouse planning requires understanding the justice system and the flow of cases to the court, as well as developing cost-effective space solutions to lessen the strain on the courthouse.




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
-1.jpg)
.jpg)

